DOI – Digital Object Identifier – Its Purpose and Applications
DOI – Digital Object Identifier
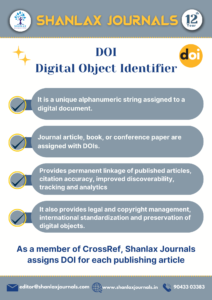
Digital Object Identifier
Unlocking the Power of DOIs:
DOI Digital Object Identifier is a unique fingerprint for digital documents. This special code, made up of letters and numbers, is assigned to things like journal articles, books, and conference papers. Imagine a digital document like a house on the internet. Its address (URL) can change just like real houses get new numbers. This can make finding it again quite a hassle! That’s where DOIs come in. They act like unique, permanent identification tags for online content, like articles, books, or reports. No matter where the “house” moves online, its DOI stays the same, ensuring you can always find it easily. Unlike regular URLs, DOIs are built to last, guaranteeing reliable access of linking to and accessing online content, particularly in the academic and publishing domains.
Purpose:
The primary purpose of a DOI is to provide a permanent and stable link to a specific document or resource on the internet. Unlike regular URLs, which can change over time or become broken, DOIs are designed to be persistent and ensure that the content they point to is reliably accessible.
Structure:
A DOI typically consists of two parts – a prefix and a suffix. The prefix is assigned to the publisher by the International DOI Foundation (IDF), and the suffix is assigned by the publisher to identify the specific document. For example, a DOI might look like this: 10.1234/abcd1234.
Registration and Assignment:
Publishers or organizations that want to assign DOIs to their content must register with a DOI Registration Agency. These agencies are responsible for allocating DOI prefixes to publishers. Once registered, the publisher assigns a unique DOI to each of its digital documents.
Metadata:
Along with the DOI, metadata is often associated with the digital object. This metadata includes information about the document, such as its title, author(s), publication date, and other relevant details. This additional information helps in accurately identifying and describing the content linked to the DOI.
Resolution:
Resolving a DOI means converting the DOI into a URL that can be used to access the actual document. DOI resolution is typically handled by a DOI resolver service provided by the DOI Registration Agency. When a user clicks on a DOI link, the resolver redirects them to the actual location of the document.
Applications:
DOIs are widely used in scholarly publishing, scientific research, and other areas where it is essential to provide a persistent and reliable link to digital content. They are commonly used for journal articles, conference papers, books, datasets, and other types of scholarly publications.
Benefits:
The use of DOIs brings several benefits, including improved citation accuracy, better tracking and management of scholarly output, and increased visibility and accessibility of research findings.



Add comment